Coughing and wheezing. That’s bronchitis for you. It can last for weeks and can be very uncomfortable, however, there are some excellent treatment options for you that can help your recovery.
In this article, you will learn what bronchitis is, its two forms (acute and chronic), signs and symptoms, risk factors, as well as conventional and natural treatment options.
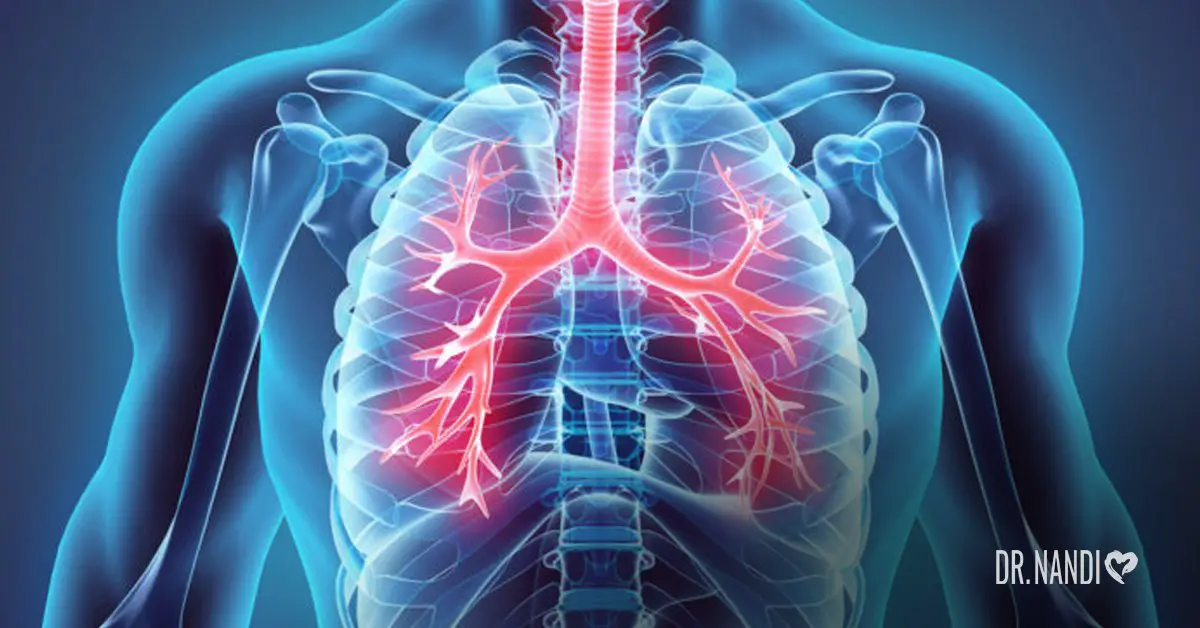
What Is Bronchitis?
About 5 percent of adults experience acute bronchitis in a year. It is the fifth leading cause for people to visit their doctors. Your bronchial tubes are the tubes that carry air to your lungs. When they are inflamed, it’s called bronchitis.
It is an uncomfortable and painful condition that causes persistent coughing, a difficult time breathing, wheezing, and chest pain. Symptoms usually last for less than 3 weeks, but in 25 percent of cases, it can last for over a month. (1)
Signs And Symptoms Of Bronchitis
Many people experience coughing and wheezing, however, bronchitis can come with many cold and flu-like symptoms. Sighs and symptoms of bronchitis may include (2, 3):
- Coughing
- Wheezing
- Shortness of breath
- Chest pain
- Sore throat
- Fatigue
- Stuffy or a runny nose
- Body aches
- Vomiting
- Diarrhea
Acute vs Chronic Bronchitis
There are two types of bronchitis: acute and chronic. Acute bronchitis is short-term and chronic is long-term.
Acute bronchitis is much more common. All symptoms completely resolve within several weeks and don’t lead to further health problems once the infection is resolved.
Chronic bronchitis is a more serious condition that occurs when the lining of the bronchial tubes are chronically irritated and inflamed. Chronic bronchitis is also associated with an accelerated decline in lung function. Smoking is the main reason that some people may develop chronic bronchitis. Avoiding smoking and second-hand smoking is essential for recovery. Viruses and bacterial infections can make the condition worse. (3, 4, 6)
Bronchitis Causes & Risk Factors
- Viruses: About 85-95 percent of cases of acute bronchitis are the result of viruses, including rhinovirus, influenza A and B, parainfluenza, and adenovirus. (5)
- Bacteria: Bacterial infections can also cause or complicate bronchitis. They usually make it more uncomfortable and more difficult to fight off. They come with more mucus and swelling than viral infections. (5)
- Weak immune systems and age: People with weaker immune systems, including infants, young children and elderly are at a higher risk of acute bronchitis and people over 45 are at a higher risk of chronic bronchitis. (3)
- Smoking: Smoking can increase the risk of chronic bronchitis and can make the symptoms and recovery from bronchitis more difficult. (6)
- Women: Women are twice as likely to develop chronic bronchitis. (3)
- Environment: Environmental factors, such as dust, chemical fumes and vapor from certain jobs, such as livestock farming, coal mining, textile manufacturing and grain handling can increase the chances of bronchitis and slow recovery. (3)
- Asthma and allergies: Asthma and allergies can make symptoms of bronchitis worse and recovery more difficult. (3)
Prevention Of Bronchitis
There are several ways to prevent bronchitis, including (3):
- Stop smoking (or don’t start) and avoid second-hand smoking.
- Get vaccinated against the flu to avoid bronchitis from the flu virus.
- Wash your hands frequently and use alcohol-based hand sanitizers to reduce the risk of catching an infection.
- Wear surgical masks if you are being exposed to dust or fumes.
- Eat whole foods, with lots of greens, vegetables, and fruits to support your immune system.
Conventional Treatment For Bronchitis
85 percent of people with bronchitis recover without specific treatment. Since it is usually caused by viral infections, there is no benefit from using antibiotics.
Bronchodilators can help to relax the bronchial smooth muscles and widen air passages to help those with asthma, allergies, breathing conditions, and smoking habits, and those with severe cases of bronchitis. However, this treatment can come with side-effects, including nausea, an upset stomach, headaches, and flu-like symptoms.
Over-the-counter pain relievers, including ibuprofen, acetaminophen, and aspirin may help with pain, however, it is important not to use them too often to avoid overdose. Always follow the directions on the box and preferably talk to your doctor before taking them. (2, 3, 7)
Natural Remedies For Bronchitis
There are countless natural remedies that can improve your symptoms and speed up your recovery, including dietary lifestyle changes, supplements, and essential oils.
Dietary Changes:
- An anti-inflammatory, whole foods diet: Eating healthy, whole foods, and an anti-inflammatory diet can strengthen your immune system, reduce your symptoms and speed up your recovery. Eat lots of greens, vegetables, and fruits that are abundant in vitamins and minerals.
- A probiotic-rich diet: Probiotic-rich foods, such as sauerkraut, kefir, kimchi, yogurt, and kombucha can help your body fight infections with healthy bacteria. Avoid processed foods, refined sugar, fried foods, and conventional dairy that can increase inflammation and mucus in your body.
- Vitamin C-rich foods: Foods rich in vitamin C, such as lemons, limes, oranges, kiwi, pineapple, strawberries, guava, broccoli, kale, and peppers can boost your immune system. (13)
- Stay hydrated: Hydration is key to recovery. Drink plenty of water, aiming for at least one glass every 2 hours. Adding herbal teas and green juices as extra can be helpful.
Lifestyle Changes:
- Use a humidifier: Humidifiers can help with airflow, reducing mucus and relieving wheezing. (8)
- Stop smoking: Smoking can increase your risk of chronic bronchitis and slow recovery. Quit smoking and avoid second-hand smoke as much as possible. (9)
- Avoid irritants: Avoid irritants, including dust, vapors, air pollution, fumes, and allergens that can make symptoms worse.
- Try pursed-lips breathing: Breath through your nose for 2 seconds then let the air out like you were to blow out a candle through pursed-lips. This can help with oxygen flow and breathing. (10)
- Rest: Getting plenty of sleep and rest is always the best medicine. Get at least 8 hours of sleep, slow down in life, take naps, relax, and stop exercising for a while.
Supplements:
- N-acetylcysteine (NAC): This can help to thin the mucus and improve lung functions, especially in the case of chronic bronchitis. (11)
- Echinacea: Echinacea is filled with antiviral properties and can help with a sore throat, pain, and headaches. (12)
- Vitamin C: It can boost your immune system and help recovery. (13)
- Probiotics: Through healthy bacteria, probiotic supplements can help in fighting infections.
- Astragalus: Astragalus is a root that can boost your immune system, fight infections and strengthen your lungs. (14)
- Ginseng: Ginseng can help improve your lung function and help with respiratory conditions. (15)
- Ginger: Ginger can reduce inflammation and help fight infections. (16)
- Turmeric: Turmeric can reduce inflammation, pain, and infections. (17)
Essential Oils
- Eucalyptus oil: It can improve your lung function and reduce inflammation in your airways. (18)
- Peppermint oil: It can clear respiratory infections and improve your condition through its antimicrobial properties. (19)
- Oregano oil: Through its natural antibacterial and antiviral properties it can fight infections, relieve symptoms and reduce inflammation. (20)
Frequently Asked Questions:
Q. How long does it take to recover from bronchitis?
A. It usually takes 2-3 weeks to recover from acute bronchitis.
Q. What happens if bronchitis is not treated?
A. Bronchitis usually clears up on its own within 2-3 weeks or a month. Natural remedies and painkillers can help. Untreated severe or chronic bronchitis can lead to further respiratory issues or pneumonia.
Q. How long are you contagious if you have bronchitis?
A. Bronchitis isn’t contagious, however, the cold, flu or infection it was caused by can be. By the time you develop bronchitis, you may not be contagious. Consult your doctor when concerned.
Q. Do I need to take antibiotics for bronchitis?
A. Most cases of bronchitis are caused by viral infections and do not require nor can be helped with antibiotics. Bacterial bronchitis may require antibiotics. Always consult your doctor.
I hope this article gave you a good understanding of bronchitis and how to treat it conventionally and naturally. If you have any questions or feedback, share in the comments sections.
References:
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2278319/
- https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/bronchitis/symptoms-causes/syc-20355566
- https://www.webmd.com/lung/understanding-bronchitis-basics#1
- https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health-topics/bronchitis
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2278319/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18303418
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2278319/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24968990
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/7497760
- https://www.copdfoundation.org/Learn-More/I-am-a-Person-with-COPD/Breathing-Techniques.aspx
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26324807
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4058675/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10543583
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22981502
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25440386
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4369959/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3535097/
- https://respiratory-research.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/1465-9921-10-69
- https://nccih.nih.gov/health/peppermintoil
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4400296/