Why is it crucial to maintain gastrointestinal health? Our gut is responsible for digesting the food we eat and absorbing the nutrients to fuel and keep our body in top condition. A healthy gut can also boost the immune system, allowing you to fight off infection from bacteria, viruses, and fungi.
Good gut health is when there is a balance between good bacteria and bad bacteria in the digestive system. When there are too many harmful bacteria, the body is under more stress leading to poor health, chronic fatigue, illnesses, and inflammation.
Signs You May Have an Unhealthy Gut
If you’re experiencing any of the following symptoms, it may be a sign that your gut is not in optimal health:
- An upset stomach
- Chronic fatigue or poor sleeping patterns
- Skin irritation
- Migraine
- Sugar cravings
- Mood changes, anxiety, depression
- Food intolerance
- Weight gain/loss
- Autoimmune conditions [1]
Common Ways to Balance Your Gut Health
One of the most effective ways to improve the balance of your gut health is by adopting a healthy lifestyle. This involves a nutritious diet, regular exercise, and proper stress management.
Here are the common ways to improve gut health:
- Drinking plenty of water to aid digestion and increase bacteria diversity
- Adding probiotics to your diets such as natural yogurt, kefir, kombucha, and kimchi
- Reducing sugar intake
- Quitting smoking
- Eating slowly to enable digestion
- Avoiding highly processed foods
- Aiming for 7-8 hours of sleep every night
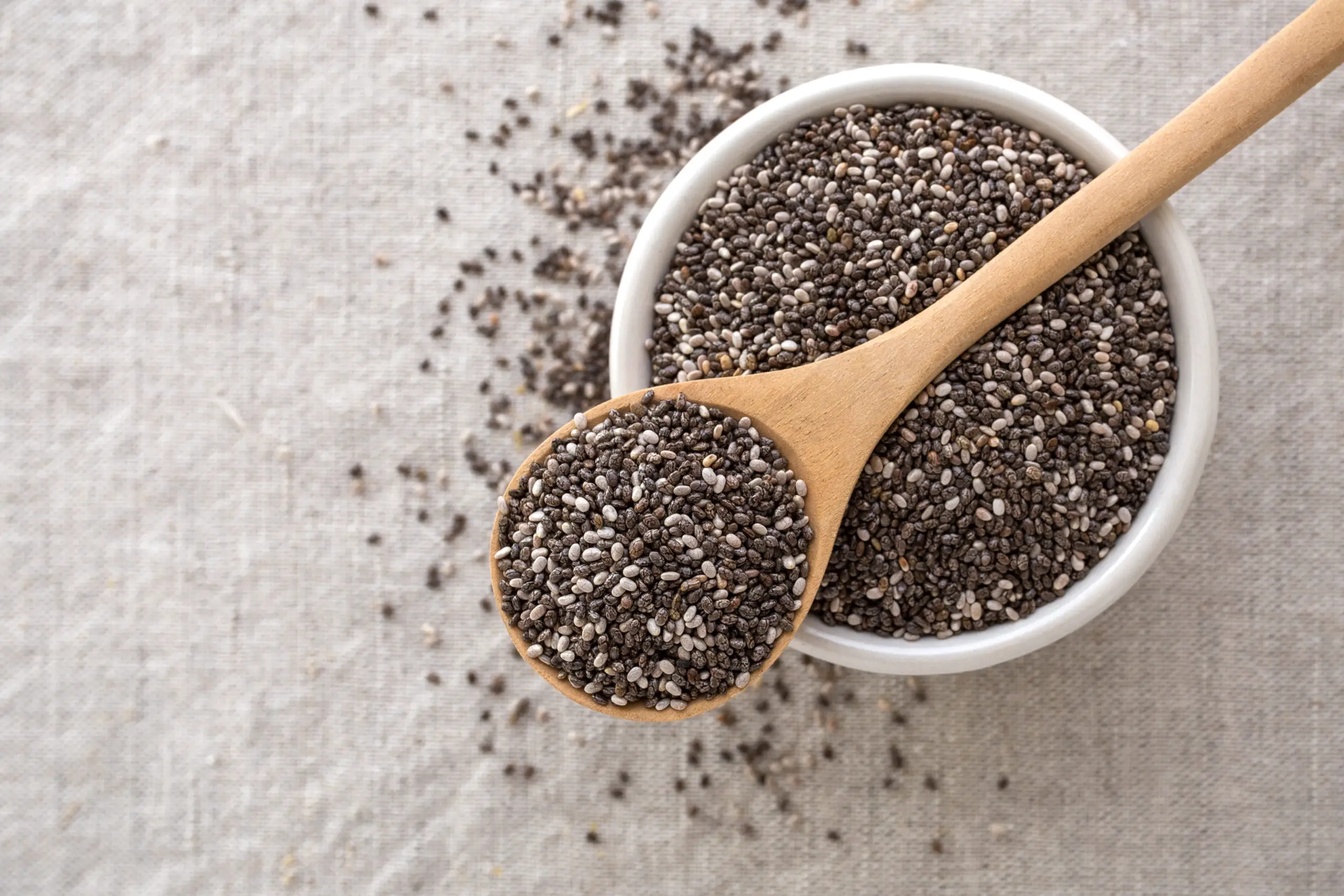
A nutritious diet is often the focus of discussions about gut health. While there are different gut-friendly foods, such as yogurt, fruits, and vegetables, chia seeds are not often the first to spring to mind.
Nutritional Value of Chia Seeds
Chia seeds are indigenous to Mexico and Central America (most notably, northern Guatemala). Also known as Salba chia or Mexican chia, the seeds are cultivated from the Salvia Hispanica species of flowering plant from the mint family Lamiaceae. [2]
Adding this superfood to your diet provides you with a rich source of vitamins and minerals such as:
- Omega-3 fatty acids
- Protein
- Fiber
- Zinc
- Calcium
- Magnesium
- Phosphorus
- Vitamin B
Chia seeds also contain amino acids that the body is unable to make on its own, such as histidine, isoleucine, leucine, and lysine. [3]

Surprising Ways Chia Seeds Can Boost Gut Health
Chia seeds are laden with dietary fiber, both soluble and insoluble. Soluble fiber acts as a prebiotic and promotes good bacteria, which helps feed gut flora that ferments into short-chain fatty acids to soothe and heal the intestinal lining from inflammation.
Insoluble fiber, meanwhile, produces less strain on the bowels and can help promote regular bowel movements. As chia seeds contain both kinds of fiber, adding them to your diet can go a long way to boosting your gut health. [4]
Here are ways chia seeds can support your gut:
Provide Antioxidants
Antioxidants are found in several foods, including chia seeds. Antioxidants protect your cells against free radicals that may increase the risk of heart disease and other medical conditions.
Free radicals are often formed as a result of natural processes in the body, such as metabolism, and can also be introduced from external sources, such as exposure to pollution, tobacco smoke, pesticides, and radiation. [5]
One of the key antioxidants found in chia seeds is a type of polyphenol called flavonoids. These compounds have been shown to have potent antioxidant activity and can help protect against oxidative stress, which is the damage caused by free radicals. [3, 6]
Protect From Heart Disease
Chia seeds are a rich source of Omega-3 fatty acids. Adding Omega-3 to your diet has been linked to a reduction in bad cholesterol, one of the leading causes of heart disease. [8]
They are also low in saturated fat, a type of fat associated with an increased risk of heart disease, making the seeds a good choice for heart health. [6]
Strengthen Bones
Chia seeds are rich in calcium, phosphorus, and magnesium, which are essential for bone strength. These seeds also contain generous amounts of Alpha-lipoic acid (ALA), which is vital for bone regeneration. [6, 7]
Support Weight Loss
Adding chia seeds to your diet may support weight loss since they are high in fiber, both soluble and insoluble. If added to your diet, they may help suppress food cravings due to an increased feeling of fullness. [8]
Lower Blood Pressure
In studies, people suffering from high blood pressure have shown a reduction in their hypertension levels after adding chia seeds or chia flour to their diet. High blood pressure is one of the main factors contributing to heart disease and stroke. [9, 10]
Improve Blood Sugar Levels
The fiber in chia seeds can also help slow the absorption of sugar into the bloodstream, which may help regulate blood sugar levels.
Further, some studies have shown that chia seeds may reduce resistance to insulin and improve blood sugar vital in the fight against diabetes type 2, heart disease, and metabolic syndrome. [11, 12]
Reduce Cholesterol Levels
Research has shown that chia seeds may reduce the amount of high-density lipoproteins (HDL; good cholesterol) and lower low-density lipoproteins (LDL – bad cholesterol) cholesterol. [13]
Chia seeds’ fiber, plant-based protein, and omega-3 content contributes to this.
Reduce Inflammation
The fatty acids in chia seeds can reduce inflammation associated with joint pain, digestive/gut health, and heart problems. [14]

Adding Chia Seeds to Your Diet
Chia seeds can be a tasty and versatile addition to your diet. They are easily incorporated into salads, smoothies, juices, and stews. They are also used as a substitute for eggs in some baked goods.
Not a fan of chia seeds? You can also use chia oil as an alternative to olive oil in salads.
You can easily add such ingredients to your dishes with the help of our free Superfood Cookbook where you can find recipes that will help improve your digestive health.
Other Uses for Chia Seeds
The cosmetic industry has been using chia oil for many years. Oil extracted from chia seeds contains 25-40% oil, with 60% containing omega-3 alpha-linolenic acid and 20% of omega-6 linoleic acid. [15]
Skincare products use chia oil to protect against:
- Premature aging
- Hair loss or thinning hair
- Harmful UV light
- Dry and cracked skin
- Clogged skin pores
It’s surprising how tiny chia seeds can offer so much nutritional value for your gut health and overall wellness. Not only that, but it’s pretty easy to tweak recipes to include this amazing superfood.
Download a free copy of the 2022 Superfood Cookbook by Dr. Partha Nandi and receive over 50 recipes that harness the power of more than 18 superfoods.
Complement your diet with supplements that boost gut health from the Health Hero Pharmacy.

Sources
- Here are the Signs of an Unhealthy Gut | GI Associates
- Chia Seeds | The Nutrition Source | Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health
- Chia Seed (Salvia Hispanica L.) – A New Age Functional Food
- Soluble vs. Insoluble Fiber: What’s the Difference?
- Free Radicals: Properties, Sources, Targets, and Their Implication in Various Diseases
- Chia Seeds (Salvia Hispanica L.): An Overview—Phytochemical Profile, Isolation Methods, and Application – PMC
- Long-chain omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid dietary intake is positively associated with bone mineral density in normal and osteopenic Spanish women
- Chia seed ( Salvia Hispanica L.) added yogurt reduces short-term food intake and increases satiety: randomised controlled trial
- Chia flour supplementation reduces blood pressure in hypertensive subjects
- Supplementation of conventional therapy with the novel grain Salba (Salvia hispanica L.) improves major and emerging cardiovascular risk factors in type 2 diabetes: results of a randomized controlled trial
- Dietary Salba (Salvia hispanica L) seed rich in α-linolenic acid improves adipose tissue dysfunction and the altered skeletal muscle glucose and lipid metabolism in dyslipidemic insulin-resistant rats
- Lipid redistribution by α-linolenic acid-rich chia seed inhibits stearoyl-CoA desaturase-1 and induces cardiac and hepatic protection in diet-induced obese rats
- Chia seed (Salvia hispanica L.) consumption and lipid profile: a systematic review and meta-analysis – Food & Function (RSC Publishing)
- Best Nuts and Seeds for Arthritis
- The Promising Future of Chia, Salvia hispanica L.