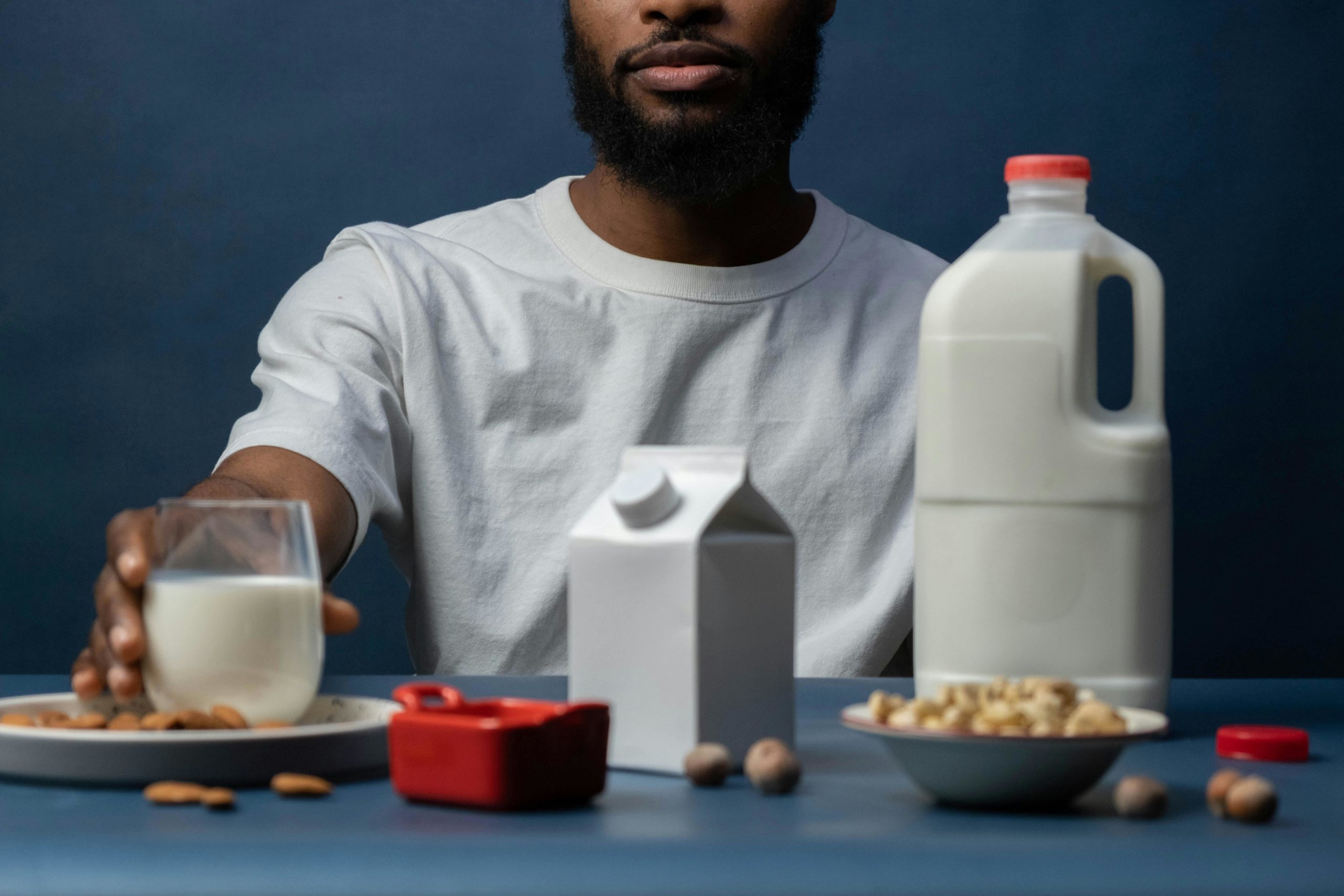
In recent years, almond milk has emerged as a star in the galaxy of health-conscious diets. As a creamy, plant-based alternative to traditional dairy milk, its popularity has soared among those looking for lactose-free, vegan-friendly options. Praised for its subtle nutty flavor and versatility, almond milk has found its way into our coffees, smoothies, and breakfast bowls. But as we embrace this dairy alternative, it’s important to peer beyond the surface – to understand what lies within these seemingly innocent cartons.
While almond milk promises a blend of health and taste, there’s more to this beverage than meets the eye. Amidst its rise, concerns about the ingredients used in commercial almond milk have stirred a pot of discussion. Some of these ingredients, while enhancing texture and shelf life, might not align with the wholesome image almond milk projects. This article seeks to unveil the truths and myths surrounding these additives, offering you the knowledge to make more informed choices.
The Rise of Almond Milk in Health-Conscious Diets
Almond milk’s journey from a niche alternative to a mainstream staple mirrors the shifting trends towards healthier, more sustainable diets. Originally a favored choice for those with lactose intolerance or dairy allergies, its appeal has broadened. Now, it caters to a diverse audience, including vegans, environmentalists, and health enthusiasts.
What makes almond milk an attractive option? Firstly, it’s plant-based, making it a sustainable and eco-friendlier choice compared to dairy milk. Its environmental footprint is considerably lower in terms of water usage and greenhouse gas emissions. Moreover, for health-conscious individuals, almond milk offers a low-calorie, low-fat alternative to cow’s milk, without sacrificing the creamy texture that milk lovers cherish.
Nutritionally, almond milk is often enriched with vitamins and minerals, compensating for what it might naturally lack compared to dairy milk. Common fortifications include calcium and vitamin D, making it a comparable choice to dairy for maintaining bone health. Additionally, its low carbohydrate content makes it suitable for those monitoring their sugar intake, like individuals with diabetes.
However, the health benefits of almond milk can vary widely based on the brand and formulation. Unsweetened versions are low in sugar and calories, making them a healthier choice. In contrast, flavored and sweetened almond milks can contain added sugars and calories, diminishing their health benefits. Thus, it’s crucial for consumers to read labels carefully to understand what they’re consuming.

Understanding Common Almond Milk Additives: Carrageenan and Others
When you pick up a carton of almond milk, the list of ingredients can be more complex than just almonds and water. Many commercial brands include additives that serve various purposes, from improving texture to prolonging shelf life. Let’s explore some of these common additives and their roles in almond milk.
- Carrageenan: Perhaps the most debated among these additives is carrageenan. Derived from red seaweed, carrageenan acts as a stabilizer and emulsifier, preventing separation and maintaining a smooth consistency. Despite being approved by the FDA, carrageenan has been at the center of health discussions. Some studies suggest it could cause inflammation in the digestive tract, potentially leading to conditions like irritable bowel syndrome and inflammatory bowel disease. However, it’s important to note that these studies have shown mixed results, and carrageenan is still considered safe by many regulatory agencies.
- Gums (Xanthan and Guar Gum): These are used as thickeners and stabilizers. Xanthan gum, produced through fermentation, and guar gum, derived from a bean plant, help in maintaining the texture of almond milk. While generally regarded as safe, some people might experience digestive discomfort from these gums.
- Synthetic Vitamins and Minerals: To mimic the nutritional profile of dairy milk, some brands add synthetic vitamins like Vitamin A palmitate and minerals. While they enhance the nutritional value, there’s debate over their absorption and efficacy compared to naturally occurring nutrients.
- Sweeteners and Flavors: Many flavored almond milks contain added sugars or artificial sweeteners, which can impact blood sugar levels and overall health. It’s essential for those monitoring their sugar intake to opt for unsweetened varieties.
- Preservatives: Ingredients like potassium sorbate and sodium benzoate are added to extend shelf life but can cause allergic reactions in sensitive individuals.
Debunking Myths: The Safety of Carrageenan
Carrageenan, a common ingredient in many almond milk brands, has sparked considerable debate regarding its safety and health effects. Understanding the science and regulatory stance on carrageenan is essential for making informed dietary choices.
What Is Carrageenan?
Carrageenan is derived from red seaweed and is widely used in the food industry as a thickener and stabilizer. Its primary function in almond milk is to improve texture and prevent ingredient separation.
The FDA classifies carrageenan as “generally recognized as safe” (GRAS) for use in food. This conclusion is based on scientific reviews and studies evaluating its safety in food products.
Health Concerns and Research
Some studies have raised concerns about carrageenan potentially causing inflammation in the digestive system. These studies suggest a link to digestive disorders such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) and inflammatory bowel disease (IBD).
However, it’s important to note that research in this area presents mixed findings. Many studies have found no significant adverse effects from consuming carrageenan in food.
Consumer Choices and Carrageenan-Free Products
Given the ongoing debate, some consumers opt to avoid carrageenan, especially those with sensitive digestive systems or specific health concerns. In response, several almond milk manufacturers now offer carrageenan-free versions of their products.
While it’s vital to be aware of potential concerns, it’s equally important to consider the broader context of dietary choices. Carrageenan is just one of many ingredients in food products, and its impact should be weighed against other nutritional factors.

The Importance of Reading Labels
Navigating the world of food labels can be a daunting task, but it’s a crucial skill for maintaining a healthy diet, especially when it comes to products like almond milk. Here’s how to become savvy about reading and understanding food labels:
- Identify Key Ingredients: Focus on the first few ingredients listed, as they make up the majority of the product. In almond milk, look for almonds and water as primary ingredients.
- Watch Out for Additives: Be mindful of added sugars, artificial sweeteners, and stabilizers like carrageenan and gums. Their presence and quantity can significantly impact the healthfulness of the almond milk.
- Understand Nutritional Information: Check the serving size and calculate the nutrients accordingly. Pay attention to calorie count, sugar content, and nutrient fortifications like calcium and vitamin D.
- Look for Allergens and Dietary Indicators: Almond milk is naturally dairy-free and vegan, but it’s important to check for cross-contamination warnings if you have allergies. Also, look for certifications like non-GMO or organic if these factors are important to you.
- Decipher Health Claims: Be cautious of health claims on packaging. Terms like “natural,” “pure,” or “healthy” can be misleading without concrete, supporting information.
- Prioritize Transparency: Choose brands that are transparent about their sourcing and manufacturing processes. This can often indicate a higher quality product.
Homemade Almond Milk Recipe
For those looking to have more control over their almond milk consumption, making it at home can be a simple and satisfying solution. Homemade almond milk is free from additives and preservatives, allowing for a pure, natural taste. Here’s how you can make it:
- Simple Ingredients: The basic components for homemade almond milk include raw almonds and water. Optional ingredients for flavoring can include a pinch of sea salt, vanilla extract, or natural sweeteners like dates.
- Soaking Almonds: Begin by soaking the almonds in water overnight. This softens the almonds and makes them easier to blend.
- Blending: Drain and rinse the soaked almonds, then blend them with fresh water. For a standard ratio, use about one part almonds to three or four parts water.
- Straining: Once blended to a smooth consistency, strain the mixture using a nut milk bag or cheesecloth to separate the pulp from the milk.
- Customization: The beauty of homemade almond milk is customization. Adjust the water to almond ratio for desired thickness, and add sweeteners or flavorings to taste.
- Storage: Store the almond milk in a sealed container in the refrigerator. It typically keeps well for a few days.
- Using the Almond Pulp: Don’t discard the leftover almond pulp. It can be used in baking, as a granola ingredient, or in smoothies for added fiber.
Homemade almond milk not only ensures a product free from unwanted additives, but it also allows for a richer, more authentic almond flavor. Plus, it’s a rewarding way to engage with what you consume, offering both health and environmental benefits.
My Personal RX on Making Informed Choices in Plant-Based Alternatives
In my practice, I often discuss the importance of informed choices in diet, particularly when it comes to plant-based alternatives like almond milk. Here are some broader tips that apply not just to almond milk but to various plant-based foods and drinks:
- Understand Ingredients: Whether it’s almond milk, soy yogurt, or any plant-based product, always read the label. Knowing what’s in your food is the first step towards healthy eating.
- Nutrient Fortification: Many plant-based alternatives lack certain nutrients found in their animal-based counterparts. Look for products fortified with essential nutrients like calcium, vitamin D, and B12.
- Be Aware of Additives: Just like with almond milk, be cautious of additives in plant-based products. Use resources like my Toxic Ingredient Guide to educate yourself about harmful ingredients and make smarter choices.
- Balancing Macronutrients: Ensure a balance of macronutrients (proteins, fats, carbohydrates) in your diet. For example, if your almond milk is low in protein, pair it with a protein-rich food.
- Homemade Versions: Whenever possible, consider making plant-based alternatives at home. This way, you control the ingredients and avoid unwanted preservatives and additives.
- Supplements for Nutritional Gaps: For nutrients that might be lacking in plant-based diets, such as Omega-3 fatty acids or iron, consider supplements like Ultra Cal-Mag for bone health.
- Consult Health Professionals: Before making significant dietary changes, especially if you have health conditions, consult a healthcare professional to tailor advice to your individual needs.
- Diversity in Diet: Don’t rely on a single source of nutrition. Include a variety of plant-based foods to ensure a well-rounded intake of nutrients.
- Eco-Friendly Choices: Consider the environmental impact of your food choices. Plant-based alternatives are generally more sustainable, but it’s also important to consider packaging and the company’s environmental policies.
- Taste and Enjoyment: Finally, choose plant-based alternatives that you enjoy. Healthy eating should also be about pleasure and satisfaction, not just nutrition.